Mastalgia, or breast pain, is something that a large number of women experience irrespective of their age. Here, it is important to note that most of the time chest pain is not associated with severe conditions like cancer. It may arise from hormonal changes, infections, or other benigh conditions. It is important to diagnose the type, reason, and intensity of pain to get the right treatment.
Symptoms of Breast Pain
- Unilateral or bilateral tenderness or pain
- Pain can range from burning to stabbing
- Feeling of fullness or heaviness in the breasts
- Cyclical pain: pain that is intensified before showing
- Non-cyclical pain: chronic pain not associated with the cycle
Causes of Breast Pain
- Hormonal Changes
Women in periods of menstruation or pregnancy often experience pain in breasts due to changes in estrogen and progesterone. This is very common in teenagers, premenopausal women, and women on hormone therapy.
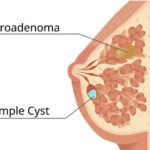
- Breast Cysts or Lumps
Painful and tender lumps within the breast tissue. Dermoid cysts are formed inside the breast tissue and can be very painful when they enlarge or get inflamed.
- Breast Infections (Mastitis)
Breast infection that occurs usually while breastfeeding due to obstruction of milk ducts. It causes redness, swelling, warmth, and possible mastalgia.
- Injury or Trauma
Breasts may ache if they suffer a direct blow or are strained around their tissues.
- Medications
In breast tenderness certain drugs, hormonal therapies, depression medications, and heart medicine, tend to cause pain.
- Fibrocystic Breast Changes
Breast tissue being lumpy or described as having a ropelike texture is more common in premenopausal women and it may result in pain and discomfort.
- Poorly Fitted Bras
Pain can occur from a bra that is worn too loosely which does not give adequate support to the breast.
Diagnosis of Breast Pain
A doctor, to assess a patient’s breast pain might suggest:
Physical Examination: Look for identification’s regarding lumps, swelling or tenderness.
Mammogram: X-ray examination aids in identifying any issues and abnormalities.
Ultrasound: Cysts and dense breast tissues are seen more with this imaging equipment.
Hormone Tests: Shifts of chemical substances that control various metabolic processes will be examined.
Biopsy: When lumps are present, a sample of a portion of tissue will be analyzed.
Treatment Options for Breast Pain
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoidance of strenuous physical activity while wearing a good supportive bra.
- Rest to alleviate stress and warm or cool flannels to be used as compresses.
- Keeping a balanced diet full of healthy foods such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Medications
- Pain relief medication that is easily accessible such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
- Severe cases of cyclical pain usually require hormonal therapy.
- Treating Underlying Conditions
- Breast pain due to an infection can then be treated with antibiotics.
- Draining or removing painful cysts if necessary.
- Cutting Down On Caffeine Or Salt Consumption
- Some women claim that reducing sodium intake and caffeine consumption alleviates their breast pain.
Final Remark
While breast pain is a common medical issue, its causes are numerous and are, for the most part, not cancerous. That being said, attending to any persistent or severe breast pain is critical, as it needs further medical investigation to rule out serious concerns.
Here at Prajnam Breast Care Centre, we strive to ensure that no woman suffers from the consequence of late-stage diagnosis or delayed therapy. Our comprehensive approach involving education, early screening, and advanced therapeutic measures empowers women with world class breast healthcare solutions. If you have any breast-related concerns or experience persistent breast pain, contact us today for expert guidance and integrated healthcare.
Treatments
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Suchana is absolutely a pleasing personality and doesn't get you tense. I am glad I came to her. Besides, she doesn't run like a business and follows ethical conduct.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Highly recommend.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Suchana was great. We were late beyond 7 pm but they were so nice they waited for us and also my wife had done with all her test. Dr also gave ample time explaining us and we were at peace. I recommend Prajam.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. The process is very humane. They are very patient and take care of all possibilities. I am glad that I found this clinic.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good experience with Dr.Suchna , she is highly knowledgeable and answers all the questions very patiently. Highly recommended for those who are looking for Breast related hospitalPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Amazing Doctor. If you are in Prajnam (Doc Suchana) you are in safe hand.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Well explained and the whole Ultrasound procedure was very comfortable