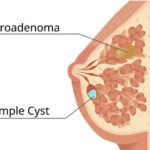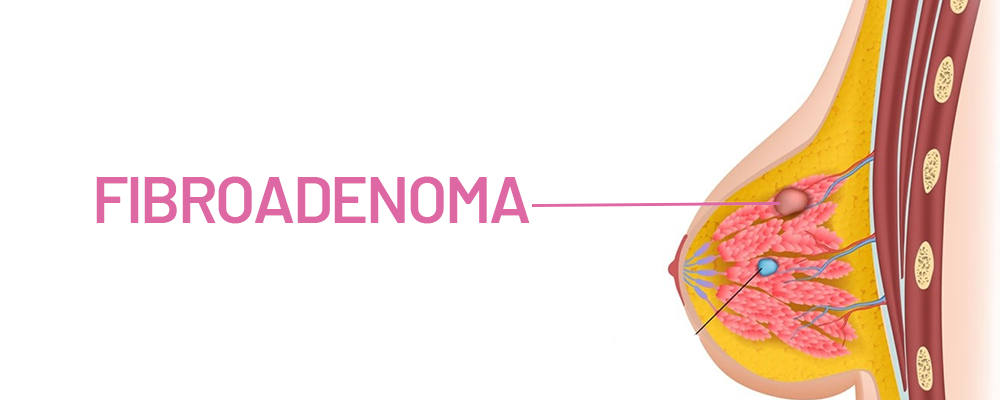
A component of breast tissue, fibroadenomas develop due to the unregulated growth of connective tissue and glandular tissue, giving rise to benign tumors, which are devoid of any malignancy and develop within the borders of the breast and are usually detected within women of younger age brackets. Even though these lumps and bumps are benign in nature and do not lead or ease into a more serious condition, it’s crucial that women remain vigilant and closely observe them to confirm that there are no resultant side effects. Having knowledge on their symptoms, causative agents, and treatment enables women to manage their breast health appropriately.
Symptoms of Fibroadenoma
- A tender, fleshy, rubbery nodule, which can be perceived with fingers as well as rounded, frictionless, tough to the core, and, when pressed, does not inflict pain.
- Blunt contours and smooth faces akin to a rubber band.
- Easy movement beneath the dermis.
- One of various lumps or bumps present; some beef up in size during pregnancy and regress after menopause.
Causes of Fibroadenoma
- This condition’s pathology is still up for debate, and there are no exact known details, but some reasons these tumors may develop include:
- Heightened level of estrogen may foster the growth of fibrous lumps within breast tissue, thus overriding dependency ratio, leading to a higher research population of women falling within the range of ages 15 to 35.
- They may increase during hormone therapy and pregnancy and shrink post-menopause when levels of estrogen drop dramatically.
- A lady with a lineage that is enigmatic of fibroadenoma appears more susceptible to developing them.
Types of Fibroadenoma
The lump tends to be soft, moves freely, and is usually not painful and starts developing. One, two, or numerous lumps may form at single or multiple sites. The most plentiful variety of breast lumps, also known as complex fibroadenomas, include simple fibroadenomas alone and are formed from breast glandular tissue and fibrous tissue and need increasing scrutiny.
- Simple Fibroadenoma
- Most common type, composed of normal glandular and fibrous tissue.
- Does not increase breast cancer risk.
- Complex Fibroadenoma
- It contains additional components such as cysts or calcifications.
- Slightly increases risk of developing breast cancer.
- Juvenile Fibroadenoma
- Appears in females between the ages of ten to eighteen.
- Tends to grow larger but with time, may shrink.
- Giant Fibroadenoma
- May grow larger than 5 cm and may need surgical intervention for removal.
Diagnosis of Fibroadenoma
Diagnosis is made clinically when an exam suggests fibroadenoma and the physician may carry out:
* Clinical Breast Examination – Palpating the breast for the size and shape of the lump within the breast and checking for its mobility.
* Ultrasound or Mammogram – Fibroadenomas may be confused for ruptured cysts or tumors during breast imaging and these procedures serve as clarifying tests for such.
* Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) or Biopsy – In the case of tumors, taking a portion of tissue aids a doctor in evaluating them microscopically.
Treatmet Options for Fibroadenoma
- Monitoring and observation
If fibroadenoma is small and is not increasing in size, it may require watchful waiting and so the doctor may opt scheduling follow-up visits instead of removal.
- Non-surgical Intervention
Change in diet – Caffeine decrease along with the following general dietary moderation has been seen to help change breasts.
Hormonal Therapy Modification – If birth control pills or other hormone-based medications are linked to fibroadenoma growth, then such will be addressed.
- Surgical Intervention (If Required)
Removal of tumor (lumpectomy) – The lump is removed when it discomforts the patient or begins to raise concerns.
Cryoablation: This technique involves freezing the fibroadenoma and hence destroying it with the extreme cold.
When to Consult a Medical Professional:
Contact a doctor if:
- The lump increases in size rapidly and/or becomes painful
- A sudden change in the size and/or shape of the breast is noticed.
- The fibroadenoma seems complex in the imaging investigations.
Final Thoughts
While fibroadenomas tend to be benign most of the times, monitoring them is helpful in detecting changes over time. If women observe any new lumpy growths or pre-existing ones that are increasing in size, medical attention must be sought.
We at Prajnam Breast Car Center understand the value of early detection combined with prompt intervention. To help maintain optimal health, we provide comprehensive screenings, diagnoses, and treatments to every woman to improve their care. In case you suffer from fibroadenomas or any breast-related distress, feel free to consult us today for proper guidance and care.
Treatments
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Suchana is absolutely a pleasing personality and doesn't get you tense. I am glad I came to her. Besides, she doesn't run like a business and follows ethical conduct.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Highly recommend.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Suchana was great. We were late beyond 7 pm but they were so nice they waited for us and also my wife had done with all her test. Dr also gave ample time explaining us and we were at peace. I recommend Prajam.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. The process is very humane. They are very patient and take care of all possibilities. I am glad that I found this clinic.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good experience with Dr.Suchna , she is highly knowledgeable and answers all the questions very patiently. Highly recommended for those who are looking for Breast related hospitalPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Amazing Doctor. If you are in Prajnam (Doc Suchana) you are in safe hand.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Well explained and the whole Ultrasound procedure was very comfortable